Unlocking the Power of A/B Testing and UX Research: Perfect Partners for Optimal User Experience
In today's competitive business landscape, delivering an exceptional user experience has become a top priority for organizations across industries. As companies strive to meet the ever-evolving needs and expectations of their users, the partnership between A/B testing and UX research has emerged as a winning combination.
By harnessing the power of data-driven experimentation and in-depth user insights, businesses can uncover the optimal user experience that drives results and sets them apart from the competition.
But how exactly do A/B testing and UX research work together to unlock this power?
In this discussion, we will explore the complementary nature of these two approaches and delve into the strategies and best practices for leveraging their full potential.
Get ready to discover how this perfect partnership can transform your user experience and propel your business forward.
Key Takeaways
- A/B testing and UX research are complementary approaches for optimizing user experience.
- UX research is essential for identifying user experience issues and providing insights for effective solutions.
- A/B testing should be conducted after a problem has been identified and a solution has been developed through UX research.
- A/B testing determines the best solution, but UX research may still be necessary for obtaining insights in certain cases.
The Complementary Nature of A/B Testing and UX Research
A/B testing and UX research are highly complementary approaches in optimizing user experience. By combining these two methods, businesses can unlock numerous benefits.
Firstly, the integration of A/B testing and UX research allows for a more holistic understanding of user behavior and preferences, leading to more informed design decisions.
Additionally, UX research provides valuable insights that can inform the development of A/B testing hypotheses and the creation of effective variations.
Case studies have showcased the effectiveness of this integration. For example, a study conducted by a leading e-commerce platform found that by combining A/B testing with UX research, they were able to increase conversion rates by 15% and reduce bounce rates by 10%.
Another case study from a popular travel website revealed that integrating A/B testing and UX research led to a 25% increase in user engagement.
The Importance of UX Research in Problem Identification
By leveraging UX research, businesses can effectively identify and address user experience issues, ultimately enhancing the overall design and functionality of their products or services.
The role of user feedback in problem identification is crucial in this process. Through qualitative data gathered from user interviews, surveys, and observations, businesses can gain valuable insights into user pain points, frustrations, and needs. This information allows businesses to identify specific problems and areas for improvement within their products or services.
Leveraging qualitative data for effective UX research enables businesses to go beyond surface-level issues and uncover deeper, underlying problems that may be impacting the user experience. By addressing these problems, businesses can create more user-centric designs and experiences that meet the needs and expectations of their target audience.
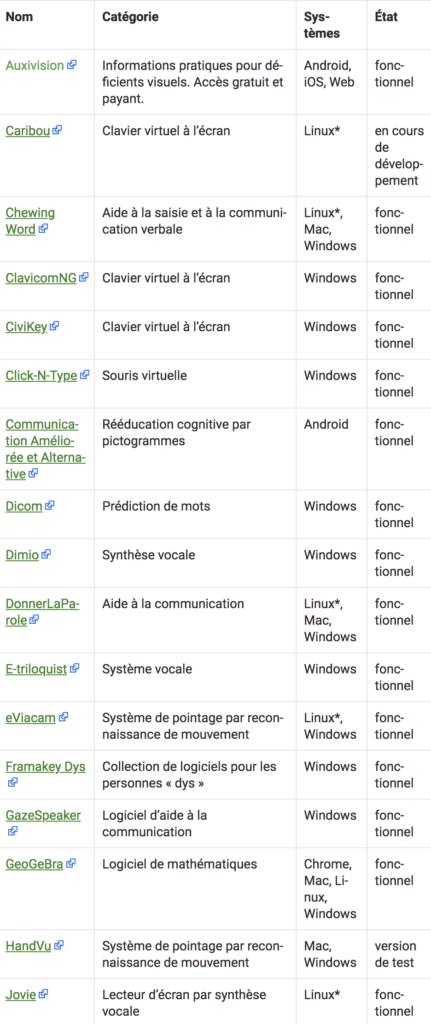
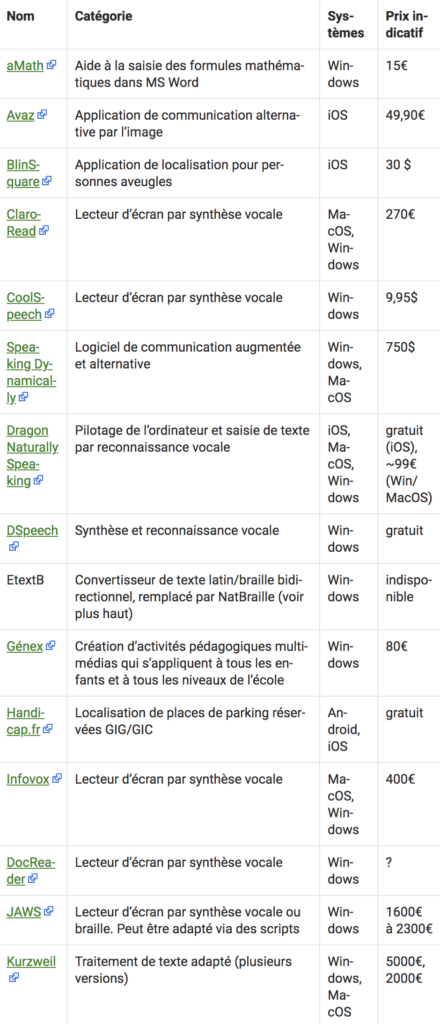
A/B Testing for Discovering the Best Solution
To determine the optimal solution, A/B testing is a data-driven approach that compares different variants to understand their impact on user experience. A/B testing requires a way to measure the success of these variants, which can sometimes be challenging for certain types of websites. However, incorporating UX research can provide valuable insights in such cases. By conducting UX research alongside A/B testing, testers can obtain a deeper understanding of user behavior and preferences, which can help in measuring the success of different variants. This can be particularly useful when testers may not notice subtle differences between page variants. The table below summarizes the challenges in measuring success and the role of UX research in overcoming these challenges.
| Challenges in Measuring Success | Role of UX Research |
|---|---|
| Limited ability to detect subtle differences between variants | Provides insights on user behavior and preferences |
| Difficulty in quantifying subjective factors such as user satisfaction | Identifies user experience issues and provides qualitative data |
| Lack of context for interpreting quantitative data | Offers contextual insights and helps in interpreting data |
Recommendations for Successful A/B Testing and UX Research Partnership
For a successful partnership between A/B testing and UX research, it is crucial to prioritize user-centricity and data-driven decision-making. Here are some recommendations for effective collaboration and overcoming common challenges in this partnership.
- Foster open communication: Establish a shared understanding of goals, methodologies, and timelines. Regularly communicate findings, insights, and test results to ensure alignment and facilitate informed decision-making.
- Collaborate from the beginning: Involve UX researchers in the early stages of A/B testing by leveraging their expertise in problem identification and solution development. This will lead to more impactful and relevant experiments.
- Combine qualitative and quantitative data: Merge the strengths of UX research (qualitative insights) and A/B testing (quantitative data) to gain a comprehensive understanding of user behavior and preferences. This hybrid approach will yield more robust and actionable results.
- Iterate and learn: Treat A/B testing and UX research as iterative processes. Continuously analyze and learn from user feedback, adapting strategies and designs accordingly. Embrace a culture of experimentation and continuous improvement.
Key Points to Remember for Optimal User Experience
To achieve optimal user experience, it is essential to prioritize data-driven decision-making and user-centricity. A/B testing and UX research play a crucial role in achieving this goal.
However, it is important to be aware of common pitfalls in A/B testing and UX research to ensure accurate results. One common pitfall is conducting A/B testing without first identifying the problem and developing a solution through UX research. Another pitfall is relying solely on A/B testing to determine the best solution without considering the insights provided by UX research.
It is crucial to remember that A/B testing and UX research are complementary approaches and should be used together for optimal user experience. Case studies have shown the significant impact of A/B testing and UX research on enhancing user experience by uncovering issues and providing insights for effective solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Some Common Challenges in Measuring the Success of A/B Testing Variants?
Measuring the success of A/B testing variants can be challenging, especially for certain types of websites. Overcoming these challenges requires finding effective ways to measure effectiveness and obtaining insights through UX research.
How Does UX Research Improve the Effectiveness of A/B Testing?
UX research improves the effectiveness of A/B testing by identifying user experience issues and providing insights on the effectiveness of different solutions. This enhances decision making and ultimately enhances user satisfaction.
Can A/B Testing Be Conducted Without Prior UX Research?
A/B testing can be conducted without prior UX research, but it may have limitations. UX research is essential for identifying problems and improving the effectiveness of A/B testing by providing insights on the best solutions.
How Many Issues Can UX Research Uncover That Affect User Experience?
UX research can uncover a significant number of issues, ranging from 50 to 100, that directly impact user experience. By identifying pain points and uncovering insights, UX research plays a crucial role in optimizing the user experience.
What Are Some Potential Drawbacks of Relying Solely on A/B Testing for Determining the Best Solution?
Potential drawbacks of relying solely on A/B testing for determining the best solution include a lack of qualitative insights and a limited scope of testing scenarios. This may result in overlooking important user experience factors and potential solution options.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the combination of A/B testing and UX research is a powerful approach to optimize user experience.
By leveraging the insights gained from UX research, organizations can identify and address user pain points, leading to more effective A/B testing.
In turn, A/B testing allows for data-driven decision-making and the validation of different solutions, resulting in a seamless and intuitive user experience.
This partnership ultimately leads to improved customer satisfaction and increased conversions.






























 – Simplicity
– Simplicity
